
On March 23th, 2021, a cargo ship operated by Taiwanese shipping company Evergreen had an accident while passing through the Suez Canal, blocking the canal strictly. On the 29th local time, the rescue team has successfully rescued the ship in the Suez Canal, but the Suez Canal still needs a few weeks to resume navigation since there are more than 300 cargo ships in line.
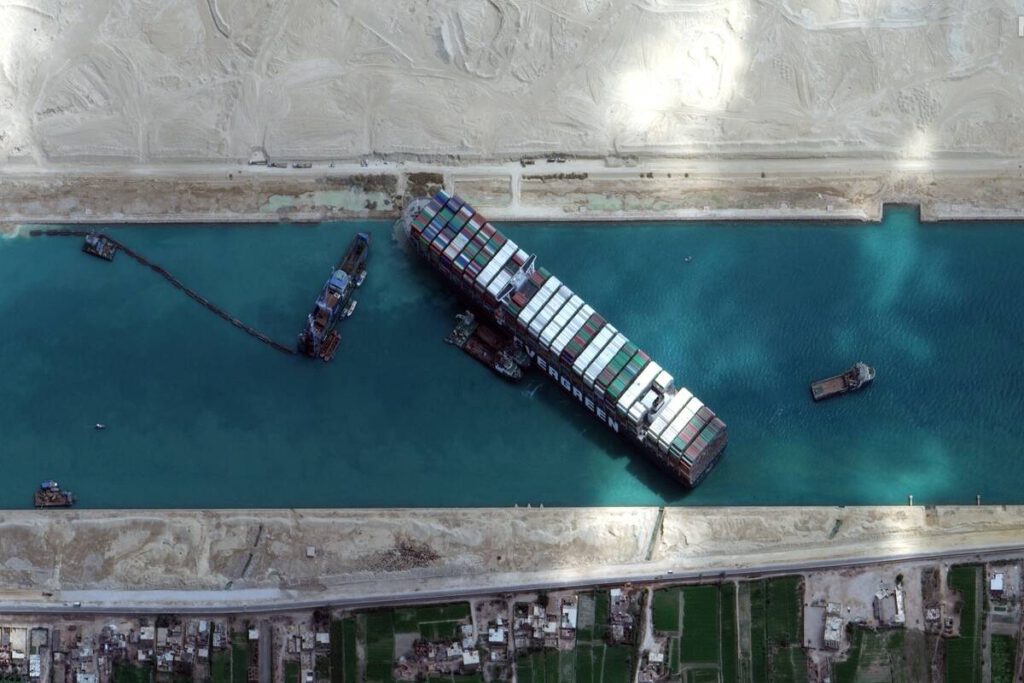

Singapore’s Lianhe Zaobao stated on the 28th that a giant oil tanker that is parked at the entrance of the Suez Canal waiting for customs clearance has to pay 30,000 to 80,000 US dollars a day for berthing. The Wall Street Journal reported that within 72 hours of the suspension of the Suez Canal, the charter price of freighters from the Middle East to East Asia has soared by 47%. To make matters worse, as many as 90% of the insurance purchased by freight does not include delays, so who should bear the losses caused by freight delays may cause disputes among the relevant parties. Osama Rabie, chairman of the Egyptian Suez Canal Authority, emphasized that the daily economic losses of the Suez Canal amounted to US$12 million to US$14 million.
The importance of the Suez Canal is determined by its geographical location. The canal is located at the border between the Sinai Peninsula and the African continent. It is a geographical hub connecting Europe, Asia, and Africa. In the era of globalization, the Suez Canal is one of the major arteries of world logistics.
According to the Wall Street Journal on the 26th, around 30% of global container transportation needs to pass through the Suez Canal annually, and the fatest and most direct shipping route between Asia and Europe is the Suez Canal.

The blockage of the Suez Canal has made global supply chain problems more prominent during the epidemic. The main cargoes transported to the north are crude oil and petroleum products, coal, ore and metals, processed metals, timber, oilseeds and oilseed cakes, and grains. The goods shipped south are mainly cement, fertilizers, metal materials and grains.
Due to the high dependence on the Suez Canal shipping channel, the European market has felt the inconvenience caused by the blocked logistics. Many European home furnishings and home appliance retailers have stated that there are goods blocked in the canal, which will lead to delayed delivery.
International rating agency Moody’s analyzes that because European manufacturing, especially auto parts suppliers, has been pursuing “just-in-time inventory management” to maximize capital efficiency and do not stock up large amounts of raw materials. In this case, once logistics is blocked, production may be interrupted.
What are possible corresponding solutions to ensure the timelessness of international shipping?
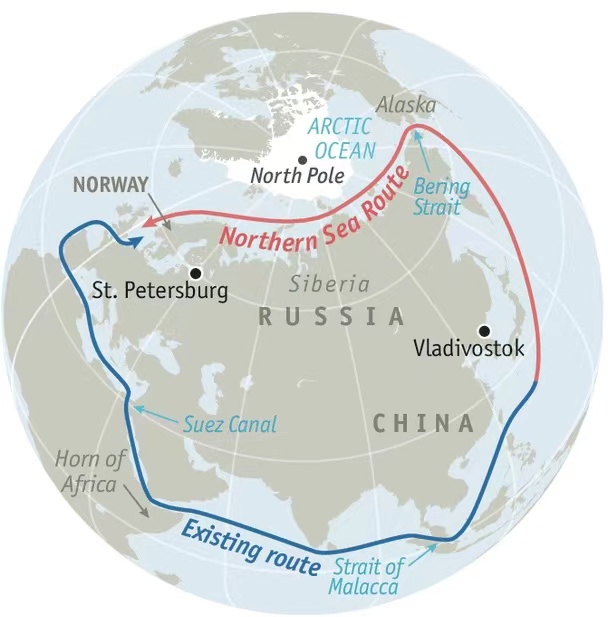
By sea, detouring the Cape of Good Hope channel or changing to the Arctic route. A detour to the Cape of Good Hope means that it will take 10 more days. The Northeast Passage from China to the North Pole through the Bering Strait to Europe can save 12 days of voyage compared to the traditional route along the Suez Canal. Unfortunately, navigation is only available in summer, and the bulk cargo must be escorted by icebreakers.
If the land transportation is changed, the rail transportation service of the new Eurasian Land Bridge, especially the normalized China-Europe Railway Express, can be a good choice. The railway speed is three times that of sea transportation, but the cost is two or three times that of sea transportation. Plus, the China-Europe Railway Express can only pull 200 boxes in one trip, and the ship that was stuck in the past two days was loaded with 20,000 TEUs. In 2020, the China-Europe Railway Express issued a total of 1.135 million TEUs. In the same year, the port throughput was 260 million, a difference of two orders of magnitude.
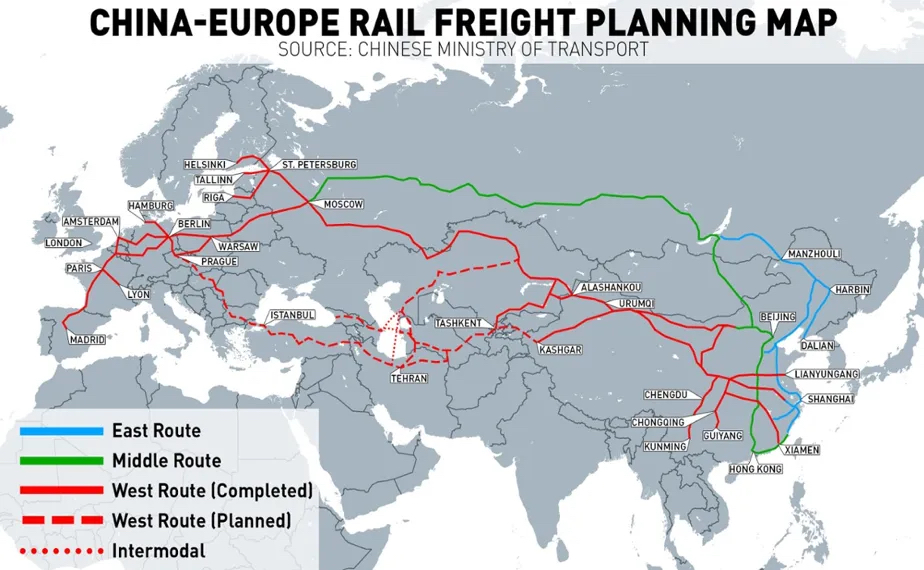
So, land transportation is a long and difficult problem, and it will not be able to replace sea transportation for a while. Moreover, even if land transportation develops in the future, sea transportation is still an important part of many countries. The volume of sea freight is large, and there is no need to repair roads. The advantage of low cost is simply invincible. They are complementary and cannot be replaced.
The Suez Canal has brought a wake-up call to Sino-European trade, and it has also sounded a wake-up call to global circulation. Expanding diversified international logistics channels will inevitably become an important way to maintain the safety and smooth flow of important international shipping channels in the future.
(Source: Chinese Ministry of Transport, the Financial Express, the Economist, BBC)



