
Huawei’s earnings report in 2021 seems to be more than ever in the limelight. On the one hand, this is Meng Wanzhou’s first appearance six months after her return to China, and on the other hand, Huawei had a challenging year in 2021.
Regarding the 2021 results, Meng said, “We have become smaller, but our profitability and cash flow access are increasing, and the company’s ability to cope with uncertainty is improving.”
Inevitable loss and continuous effort in 2021
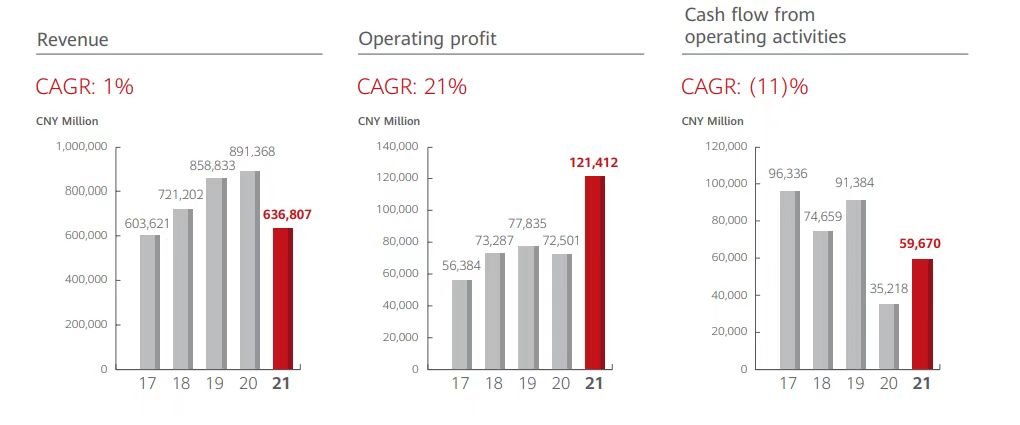
According to Huawei’s 2021 earnings report, Huawei earned CNY 636.8 billion in revenue last year, an achievement that exceeded expectations. But it has to be admitted that sales revenue in 2021 has fallen to a level close to that of 2017 when comparing financial data from the past five years. Last year’s revenue fell 28.6% year-on-year, the first time in nearly a decade that revenue growth was negative.
The reason for this is that the consumer business, which once held up half of the total revenue, has become the main factor in Huawei’s big drop in 2021. The annual report shows that Huawei’s consumer business revenue in 2021 was CNY 243.431 billion, down 49.6% year on year.
In response, Guo Ping, Huawei’s rotating chairman, said, “The consecutive years of U.S. sanctions have had a very significant impact on Huawei’s consumer business.”
The top priority of Huawei’s consumer business is the cell phone business, but Huawei has been reduced to nobody in the cell phone market. According to Counterpoint Research, Huawei’s cell phone sales in China fell 73% in the fourth quarter of 2021, leaving it with a 7% market share.
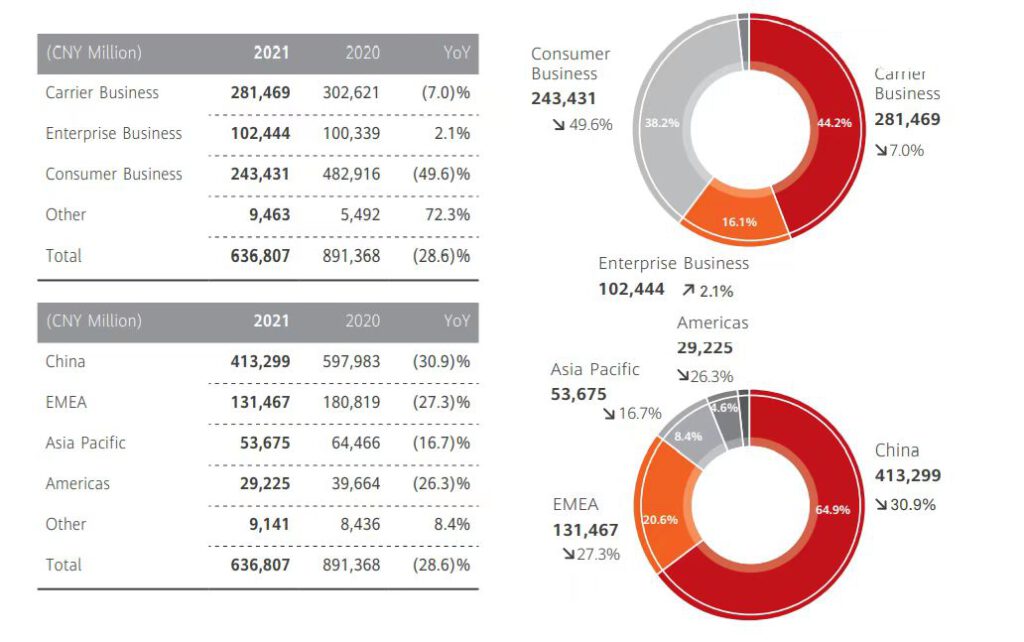
In addition, the annual report shows that Huawei’s carrier business was CNY 281.469 billion in 2021, down 7% year-on-year. In response, Meng said that China’s 5G construction had been largely completed in 2020, so there is a significant reduction in demand for 5G deployment in China.
Among the three major businesses, the only growing enterprise business revenue reached CNY 102.244 billion. In addition, Meng mentioned that Huawei Cloud and Digital Energy, two new businesses, had revenue growth of more than 30%.
Net profit, on the other hand, was CNY 113.7 billion, bucking the trend by 75.9%, mainly due to net gains from the sale of two major companies, Honor and XFusion.
Huawei’s revenue became less, but its investment in R&D did not decrease, but also began to switch ideas to broaden more revenue channels.
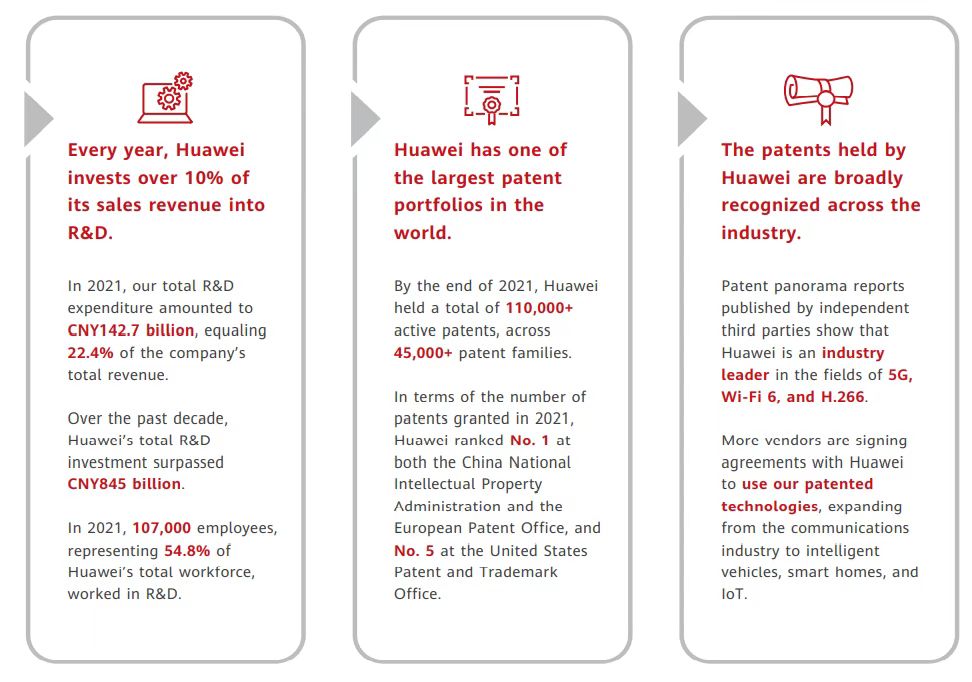
In 2021, Huawei invested CNY 142.666 billion in R&D, up 0.5% year-on-year, with a cumulative investment of more than CNY 845 billion in R&D over the decade.
The annual report shows that the number of Huawei devices equipped with HarmonyOS exceeds 220 million; HarmonyOS Connect has more than 1,900 ecological partners, with more than 4,500 certified products, and the number of new products shipped in 2021 exceeds 115 million units.
At the same time, last year, Huawei set up 15 legions for coal mining, intelligent highways, data center energy, sports and health, and other industries. These legions are at the same level as Huawei’s current three BGs and can deploy all the company’s research and development resources.
What are Huawei’s strengths?
One of Huawei’s breakthroughs is the Huawei Cloud. Guo and Meng repeatedly mentioned the cloud business: 2021 revenue of 20.1 billion, an increase of 34%. ICE domestic second, the world’s fifth, the future target direction is the data center and accelerated network.

Another breakthrough is the intelligent photovoltaic business, Huawei report deliberately invited two journalists from the Middle East and Indonesia. To plan for future industrial transformation, Saudi Arabia and the UAE have invested a lot of resources in the photovoltaic business, and actively promote carbon-neutral plans to maintain industrial advantages.

In their eyes, Huawei can provide the technology package of “photovoltaic + data center + other new technologies.” Data centers and cloud business meet their needs for industrial upgrading, and the development of the PV industry solves their urgent energy needs.
It is for these reasons that the UAE has previously reacted violently to U.S. interference in Huawei’s business. On the surface, the two sides fought for the base station and F35, but the United States tossed Huawei, affecting the UAE’s hundred-year project, which is much more important than military sales to the UAE.

Another place that envisions Huawei’s long-term plan is Indonesia. With a population of hundreds of millions, Indonesia has an adequate primary industry base and a thriving tertiary industry. Since Indian President Modi’s nationalist politics triggered an exodus of Chinese investment, a large number of Chinese venture capitalists have smashed their capital into Southeast Asia.
However, Indonesia’s capital Jakarta has an exploding population, several major islands have mismatched infrastructure development, and the country lacks technical talent. So Indonesia has been promoting a “New Capital Project” and various forms of talent development programs.
Huawei is assisting the project, laying network cables to remote areas, and training 100,000 technical talents in 5 years. If there is any problem, it is whether Indonesia can be trustworthy and remit money on time. As for the anti-China issue, Indonesia prefers to jump between China and Japan in terms of industrial capital, which is also the policy inertia of Southeast Asian countries.
Making improvements, not reaching perfection
Huawei’s strategy is clear: remove unnecessary assets, raise sufficient monetary resources to make a breakthrough in the infrastructure industry, because these industries will not be so eye-catching, and also to reduce the probability of being attacked as much as possible, and bring better revenue after the breakthrough.
Since Huawei now focuses on infrastructure, Huawei’s biggest challenge is time. Due to the unfavorable external environment and the gradual decrease in asset sales into the accounts, Huawei needs to make stable results in the relatively short period in the future to support the super 20% of the R & D ratio, otherwise, Huawei will be difficult to survive.
(Source: Huawei)



