
Four China’s central departments related to national development, energy, and information has agreed to start the construction of national computing hub nodes in several important cities and areas including Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Yangtze River Delta, Guangdong, Hong Kong, Macao Bay Area, Chengdu, Chongqing, Inner Mongolia, Guizhou, Gansu and Ningxia.
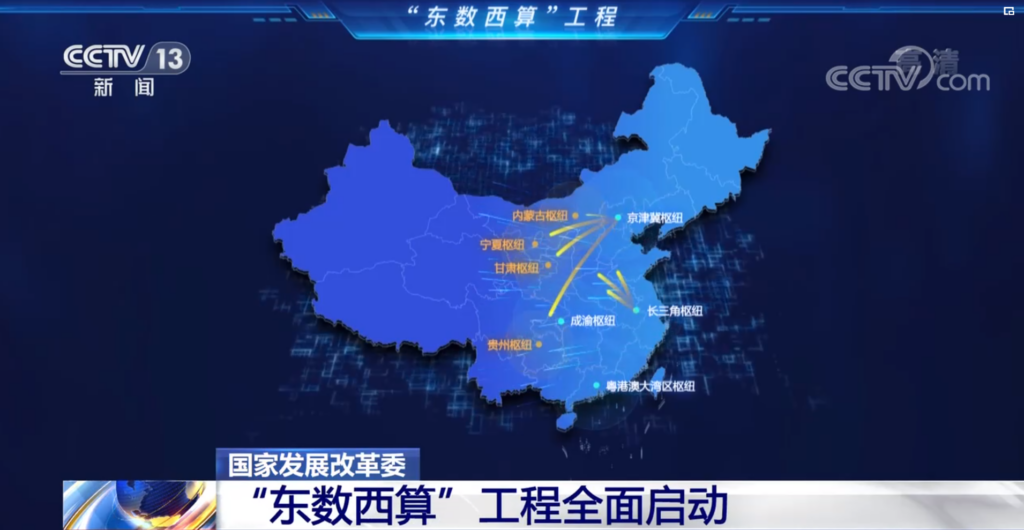
The joint decision is mainly to develop data center clusters and carry out synergistic construction between data centers and networks, cloud computing, and big data. The nation’s preliminary plan is to maintain the average annual growth rate of the national data center rack-scale at about 20% by the end of 2023 and strive to increase the average utilization rate to over 60%, with the total computing power exceeding 200 EFLOPS and the percentage of high-performance computing power reaching 10%. The national hub nodes will account for more than 70% of the computing power.
Sun Wei, deputy director of the Department of High Technology of the National Development and Reform Commission, said that the western region of China is rich in resources, especially renewable energy, with the potential to develop data centers and undertake the demand for arithmetic power in the east.
The Algorithm, like the agricultural era of water, the industrial era of electricity, has become the core productivity of the development of the digital economy, is an important infrastructure for national economic development. The implementation of the “East and West Calculation” project, to promote the reasonable layout of data centers, supply and demand balance, green intensification, and interconnection, will improve the overall level of China’s computing power, promote green development, expand effective investment, and promote regional coordinated development.

It is understood that China’s national level will promote the hub nodes to establish a sound work coordination and promotion mechanism as soon as possible, strengthen the green development requirements of data centers, and promote more data centers to move to the west where renewable energy is more abundant.
The specific action plan also includes network quality upgrade, computing power enhancement and empowerment, industry chain stabilization and enhancement, and green low-carbon development, which also focuses on the issue of carbon peak and carbon neutral.
“Currently, the use of ‘green power’ in data centers accounts for about 20% of total energy consumption. Through the ‘East Data, West Calculation’ project, the use of green energy such as photovoltaic and wind power by the data center industry in the west can be increased. emissions at this critical point in 2025 would be equivalent to 1.6 of Beijing’s total carbon emissions,” said Xu Bin, deputy director of the Center for Innovation-driven Development of the National Development and Reform Commission.
Good project with technical challenges
China is encouraging key industries to use new infrastructure such as green data centers to achieve energy saving and consumption reduction. Newly built large and super-large data centers will have a power utilization efficiency of no more than 1.3. By 2025, data centers are expected to generally have a power utilization efficiency of no more than 1.5.
In this nationwide unified arithmetic layout, there is a certain technical difficulty regarding the architecture design, cooling measures, and PUE index of data centers, which requires the use of cutting-edge advanced technologies. Zhang Hao, deputy director of Department of Network and IT Technology, China Mobile Research Institute, said that this is a major practice in the field of cutting-edge technology, which will benefit the whole industry and people’s livelihood.

And the favorable policy will bring some new development opportunities. As an industry with key demand for computing power, the AI industry will also usher in new development opportunities.
First, AI chip R&D companies will benefit from it. These companies provide rendering, training, and other functions by fixing AI-related algorithms and models to the chip. In the process of data center construction, the scale application of AI chips will be involved, which will naturally bring great benefits to AI chip R&D enterprises. The future of the project will consider the construction of the Smart Computing Center, which is a cluster of high-performance AI chips, a potential opportunity for the AI chip industry practitioners to explode, for research and development, sales and to accelerate the commercial process will have a great driving effect.
The second point is that the construction of intelligent computing centers is more demanding than ordinary data centers, and there are many new requirements for their internal design, power supply, architecture, and AI board design, so it will also bring many new opportunities for some traditional data center builders.
The third and core point is that AI algorithm engineers and AI application developers will all benefit from this. The industry needs to train a lot of AI algorithm models, which requires a lot of AI computing power, and AI computing power is very expensive. When the project data center is completed, the cost of AI computing power will be reduced, which is equivalent to reducing the development cost of AI technology and applications and improving the R&D efficiency of the AI industry.
Deeper digitalization and talents need
Guiyang Gui’an has been one of the Chinese regions with the largest number of mega data centers in the world before the launch of the project. Some international big data enterprises such as Apple, Microsoft, Intel, HP, Dell, Alibaba, Huawei, Tencent, Baidu, and Jingdong have settled in Guizhou.
But the previous data center is basically in a rough development stage, lacking overall planning, not enough regulation, with old equipment and high energy consumption. Zhang Hao said that after the launch of the project, the original scattered small and old server rooms may be revamped.
The situation that a large number of enterprises build their own, without considering carbon emission targets, power consumption, and other factors, and only worrying about business needs, will be permanently broken. The overall construction of data centers in the future must be a situation of differentiation, complementary and synergistic development.
In the context of the current society-wide vigorous promotion of digital transformation worldwide, the project has become a key part of accelerating the digitalization process in China. However, in the rapid development of the industry at the same time, the shortage of digital application of talent is also increasingly prominent.
According to China’s Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security, there is a large gap in China’s artificial intelligence talent, the domestic supply and demand ratio is 1:10, indicating a serious imbalance between supply and demand ratio. Continuously strengthening the training of talent, to make up for the shortboard of talent has become an urgent task.
The same is true for the project. The overall design, network design, maintenance and operation of the data center require a large number of professionals. Zhang Hao said, “Whether from the perspective of technological innovation or digital economy, the training and capacity enhancement of digital talents are the most critical issues. This is equivalent to the fact that if your weapons are advanced, but your human capabilities cannot keep up, you may not be able to use them well. Only by combining the two into one and moving forward in tandem can the role of cutting-edge technology be better utilized.”
(Source: Xinhua, CCTV 13, China’s government)



