
On June 6, 2019, China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology officially issued 5G commercial licenses to the four major operators of China Mobile, China Unicom, China Telecom, and China National Radio and Television Administration, opening the 5G era of China’s communications industry.
By the end of June 2022, the cumulative number of 5G base stations in China reached 1.854 million and 5G terminal users reached 455 million, accounting for more than 60% of the world’s total. Operators have invested more than 400 billion yuan in 5G. China’s typical 5G scenarios have also been integrated into 40 of the 97 major categories of the national economy.

Accelerating operators’ 5G investment and construction
According to China Academy for Information and Communications Technology, 5G directly drove a total economic output of 1.3 trillion yuan in 2021 and economic value of about 300 billion yuan. The cumulative investment in 5G network construction in China will reach 1.2 trillion yuan in 2025, driving-related investment of more than 3.5 trillion yuan, directly creating more than 3 million jobs, driving more than 8 trillion yuan of emerging consumption, and forming a trillion-level 5G related products and services market.
Liu Liehong, Chairman of China Unicom, introduced that 5G has become an important engine to drive the development of the global digital economy. As of June this year, more than 220 commercial 5G networks have been deployed in 86 countries and regions worldwide, and the number of 5G users has exceeded 740 million. Among them, the number of 5G base stations in China has exceeded 1.85 million, the number of 5G cell phones has exceeded 450 million, and 5G applications cover 40 major categories of the national economy.
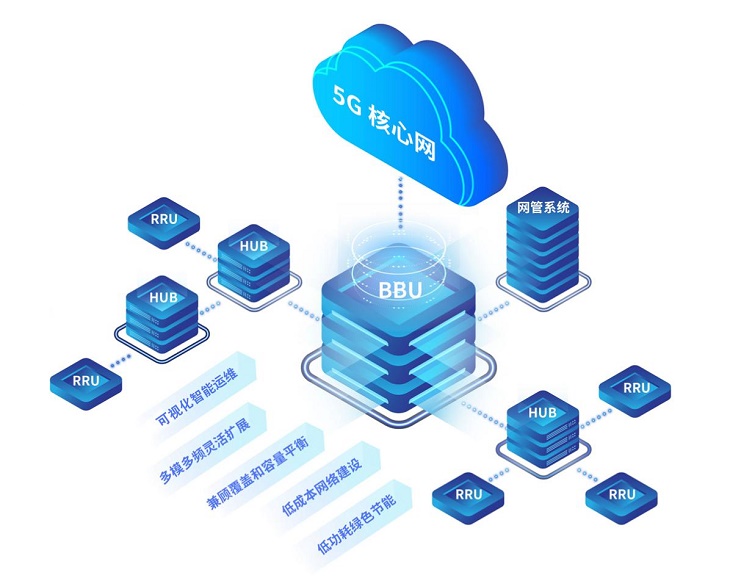
Ke Ruiwen, Chairman of China Telecom, introduced that China Telecom and China Unicom have built and shared the world’s first, largest, and fastest 5G SA shared network, opened 870,000 5G shared base stations, and achieved basic continuous coverage in key towns and villages. Through the shared base stations, the two sides have saved a total of 240 billion yuan in investment, more than 20 billion yuan in annual operating cost savings, more than 10 billion kilowatt hours in electricity savings, and more than 6 million tons of carbon emissions reduction.
Yang Jie, Chairman of China Mobile, said that China Mobile has opened more than 1 million 5G base stations, accounting for more than 30% of the total number of base stations worldwide. China Mobile’s 5G package customers have exceeded 500 million households.
Song Qizhu, Chairman of China National Radio and Television Administration, revealed that so far, China National Radio and Television Administration has built and shared 850,000 5G base stations with China Mobile, and will soon share 1.91 million 4G base stations, and has fully interconnected with China Telecom and China Unicom. On the terminal side, China Radio and Television have 327 cell phones fully supporting the 700 megabit band, and 95% of the new cell phones on the network support several hundred megabit bands, and plans to fully complete the adaptation and upgrade of high stock 4G and 5G terminals by the end of September.
Promote 5G applications in more vertical industries
“There have been three years of 5G commercialization, and China’s 5G construction has met expectations, but the maturity of related technologies still needs to be improved, and the ability of 5G to provide large bandwidth, low latency, wide coverage, and large connectivity has not yet been undertaken by more mature business applications,” commented Wu Hequan, academician of the Chinese Academy of Engineering.
The process of further deepening 5G construction and application cannot be achieved without the group efforts of the whole 5G industry chain, including chips, terminals, system equipment, operators, industry users, etc.
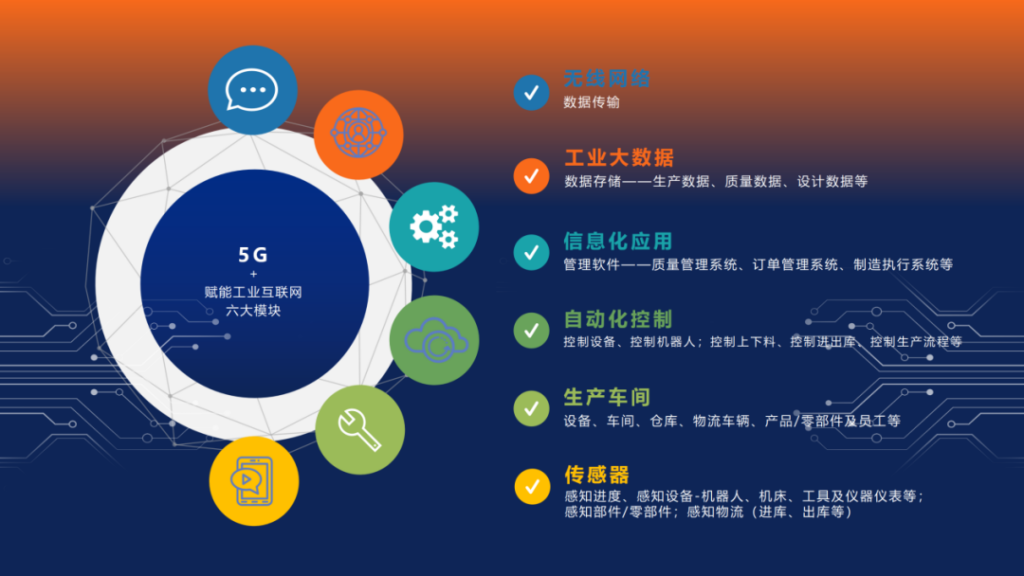
Industry convergence application is a worldwide problem. There are difficulties in the integration of 5G with vertical industries, such as difficulties in cross-sector integration, lack of clarity in business models and technical solutions, technical standards, etc. This will affect the role of 5G in driving thousands of industries.
Take the 5G industrial module as an example, as an important basis for accelerating the construction of new industrial networks, it provides a channel for broadband wireless access applications such as HD video/AR and VR for industrial scenarios. However, many experts say that the economy, versatility, and reliability of industrial 5G modules are still the important bottlenecks that restrict the large-scale application of industrial 5G.
Can the meta-universe bring an application explosion?
The meta-universe concept has been hot since the second half of last year, and a meta-universe forum was set up for the first time at this year’s World 5G Congress. Telecom operators, terminal equipment manufacturers, and various research institutions are also jointly laying out.
Tan Jianrong, academician of the Chinese Academy of Engineering, pointed out that the metaverse will create a new situation in Internet development and push the network into the Web 3.0 era. All current Internet applications need to be upgraded in 3D, and there are bound to be brand new applications and business models. Energy, agriculture, finance, real estate, vocational education, and other areas will be the development space of metaverse in the future. However, metaverse from concept to landing still needs to strengthen the source and expansion of metaverse resources, talent training, hardware construction, and other all-around collaborative building.

The industry also put forward cold thoughts on the metaverse. Wu Hequan frankly said that the meta-universe in a narrow sense is based on the technologies of VR, AR, and MR, integrating user avatars, content production, social interaction, online games, virtual currency payments, and other cyberspace, which is the integration of a series of modern information technologies, but also has higher-level requirements. Moreover, the metaverse will also involve higher-order applications such as hologram and sensory interconnection, which require higher bandwidth. The future metaverse may have thousands of concurrent volumes and user throughput may reach TB, and it is still difficult to meet the needs of application implementation with the current level of 5G development alone.
Mao Shijie, vice president of Lenovo Group, pointed out that Shanghai, Guangzhou and many other cities have issued relevant policies to encourage the promotion of the integration of the meta-universe with the real economy. With the advantage of the whole value chain of China’s manufacturing industry, China can build a virtual digital factory based on the existing factory information system through scanning and data collection, and complete the exploration of the whole value chain to advance the usage of 5G in the metaverse.
(Source: Mobile World Live, CGTN)



