
As 2022 s approaching, the past year has been a rewarding one for the science and technology community. The Chinese science and technology community has even made some important breakthroughs.
Retrieving the “ancestral” genes of rice
Polyploidy is an important mechanism of plant evolution. The cultivated rice grown today has undergone thousands of years of artificial domestication, with continuously improved agronomic traits, while a large amount of genetic diversity has been lost, resulting in a lack of superior genetic resources.

Published on Cell, Li Jiayang’s team at the Institute of Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences has broken through the technical bottlenecks of genome resolution, efficient genetic transformation, and efficient genome editing, annotated a series of domestication genes and important agronomic traits genes in the genome of wild allotetraploid rice, and successfully created a variety of genome-edited wild allotetraploid rice with reduced grain fall, shorter awn length, reduced plant height, longer grain length, thicker stalk, and shorter tassel time in different degrees.
Achieving quantum superiority in two physical systems
In February, Science Advances published the results of a new programmable silicon-based optical quantum computing chip developed by Chinese researchers to achieve a variety of quantum algorithms for solving graph-theoretic problems, which is expected to gain future applications in areas such as big data processing.
In May, Science published that Chinese researchers from the University of Science and Technology of China successfully developed a 62-qubit programmable superconducting quantum processor, called Zu Chongzhi. In October, the team further developed the processor that achieved 66-qubit in a two-dimensional array in a tunable coupler architecture.

At the same time, the upgraded version of Jiuzhang 2.0, a new light-based quantum computer prototype that can implement large-scale Gaussian boson sampling (GBS) 1 septillion times faster than the world’s fastest existing supercomputer.

With the emergence of Jiuzhang 2.0 and “Zuchongzhi 2.1, China has become the only country to realize the superiority of quantum computing in two physical systems.
China’s Sky Eye welcomes international scientists
The 500-meter aperture spherical radio telescope (FAST), a major national science and technology infrastructure known as the China’s Sky Eye, invites astronomers from around the world to apply for observation.

Located in Guizhou Province, completed in 2016, FAST is the world’s largest single-aperture, a most sensitive radio telescope with independent intellectual property rights. Radio telescopes and optical telescopes are similar, the larger the aperture received the more electromagnetic waves, the higher its sensitivity, the stronger the detection capability. With this, FAST can receive the faint radio signals in the universe.
China made large-scale cryogenic refrigeration equipment
China is a large country using large cryogenic refrigeration equipment. But due to the lack of large cryogenic refrigeration systems, key sub-equipment and integrated technology, China’s large-scale cryogenic refrigeration equipment has long relied on imports.

In 2015, the Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry of Chinese Academy of Sciences (TIPC) started the development of large cryogenic refrigeration equipment from liquid helium to superfluid helium temperature zone. In 2021, the overall technology of the project reached the international advanced level. This marks that China has the ability to develop large cryogenic refrigeration equipment of 1000-watt level for liquid helium (-269℃) and 100-watt level for superfluid helium (-271℃).
Light storage time reaches 1 hour, heading to quantum U disk
In April, the research group of the University of Science and Technology of China improved the optical storage time to 1 hour, significantly refreshing the world record of 1 minute of optical storage set by a German team in 2013, and taking an important step toward the realization of quantum USB flash drives.

Artificial sun set a new world record
The light and heat on which everything on Earth depends for growth originate from the energy released by the sun’s nuclear fusion reaction. If we can create an artificial sun with a similar nuclear fusion process to generate electricity, mankind is expected to achieve complete energy freedom.
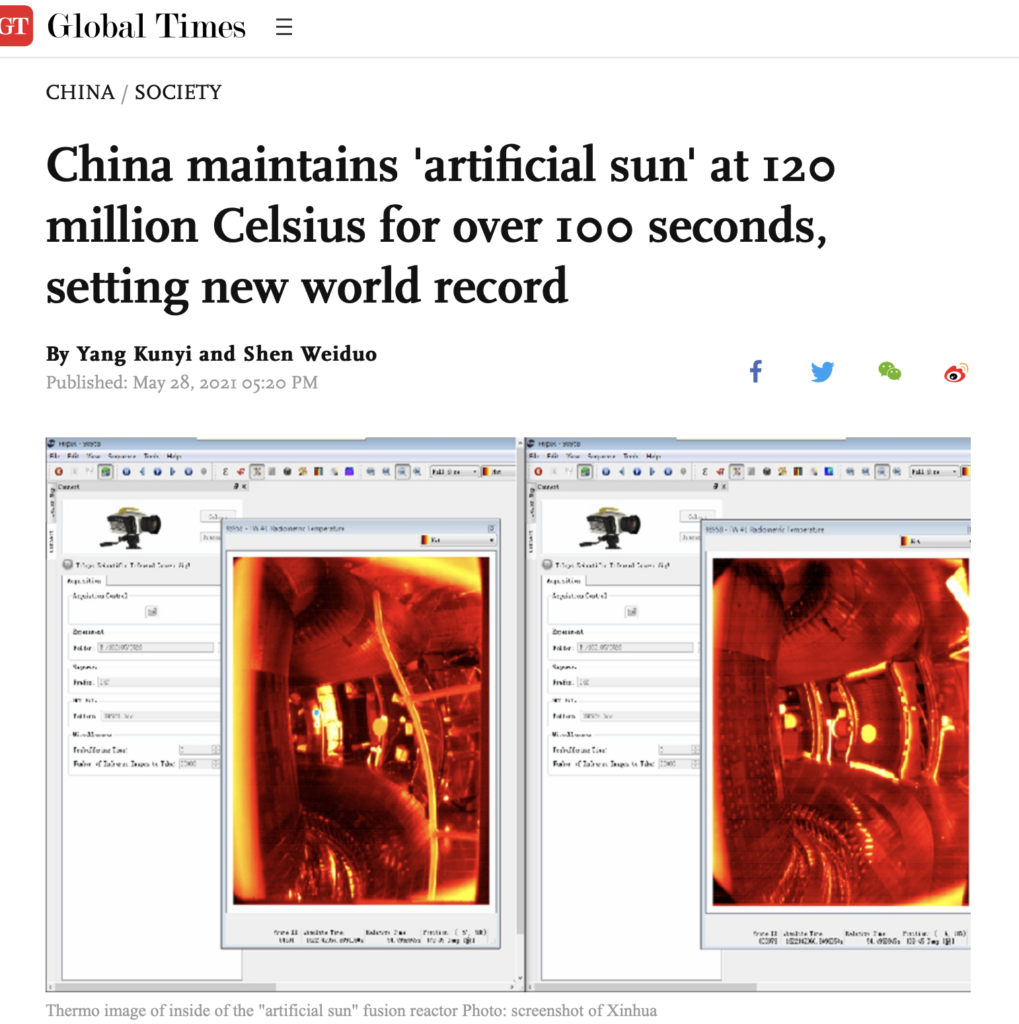
To achieve the conditions required by the nuclear fusion experimental device, Chinese scientists innovated independently, designed and developed most of the key technologies with independent intellectual property rights, and creatively completed the overall engineering design of the mainframe of the Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST). In May, EAST successfully achieved a repeatable 120 million degrees Celsius for 101 seconds and 160 million degrees Celsius for 20 seconds of plasma operation, creating a new world record for tokamak experimental device operation and taking an important step toward fusion energy applications.
Virtual Earth laboratory launched
In June, China’s first Earth system simulation device, EarthLab, with independent intellectual property rights was launched in Beijing’s Huairou Science City.

The virtual Earth lab is a numerical simulation of the Earth system, which uses the description of the physical, chemical, and life processes of the Earth system and its evolution of the laws on a supercomputer for large-scale scientific calculations. This enables scientists to recreate the Earth’s past, simulate the Earth’s present, and predict the Earth’s future.
Optical fiber with bendy ice
In July, Chinese and American researchers created a bendy fiber made from ice in a -50 ℃ environment. It is capable of both flexible bending and low-loss light transmission and is similar to glass optical fiber in terms of performance.
Optical fiber, as a functional structure that confines and freely transmits light, is currently one of the most effective tools for light field manipulation. Therefore, the preparation of optical fibers from ice has wide application prospects.
Synthesis of starch without photosynthesis
Starch is mainly synthesized by green plants by fixing carbon dioxide through photosynthesis. In crops such as corn, the conversion of carbon dioxide into starch involves more than 60 steps of metabolic reactions and complex physiological regulation, and the theoretical efficiency of solar energy utilization is no more than 2%. The cultivation of crops requires a cycle of several months and uses large amounts of land, freshwater, fertilizers, and other resources.
To improve production efficiency, Chinese researchers have achieved the first total synthesis from carbon dioxide to starch molecules in the laboratory. The starch synthesis rate of this artificial pathway is 8.5 times higher than that of corn starch synthesis. Under the condition of sufficient energy supply, according to the current technical parameters, the theoretical annual starch production of 1 m3 of bioreactor is equivalent to the average annual production of corn grown on 20234 m² of land in China.
Prove the core conjecture of Kähler metrics
In November, Chinese mathematicians Xiuxiong Chen and Jingrui Cheng achieved a milestone result in the field of partial differential equations and complex geometry by solving a fourth-order completely nonlinear elliptic equation, successfully proving the mandatory conjecture and the geodesic stability conjecture, two core conjectures that have been outstanding in the international mathematical community for more than 60 years, and solving several conjectures concerning the curvature of constant scalars on Kähler manifolds.

(Source: Cell, Science Direct, Global Times, American Mathematical Society, Nature)



