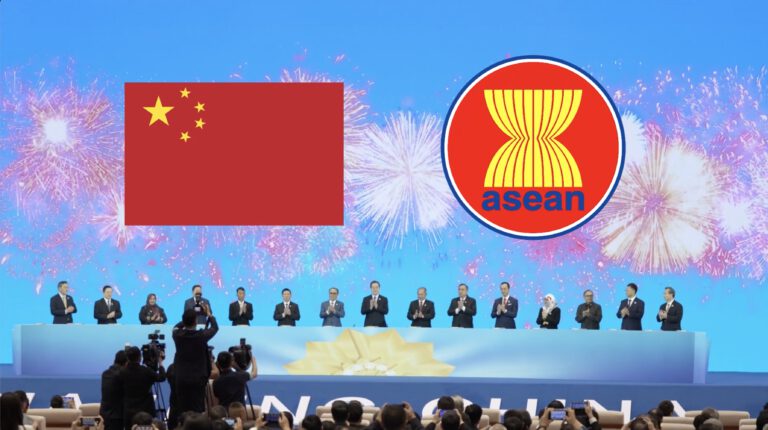
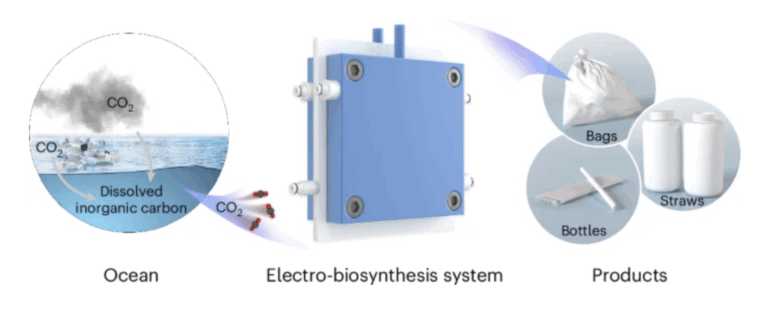
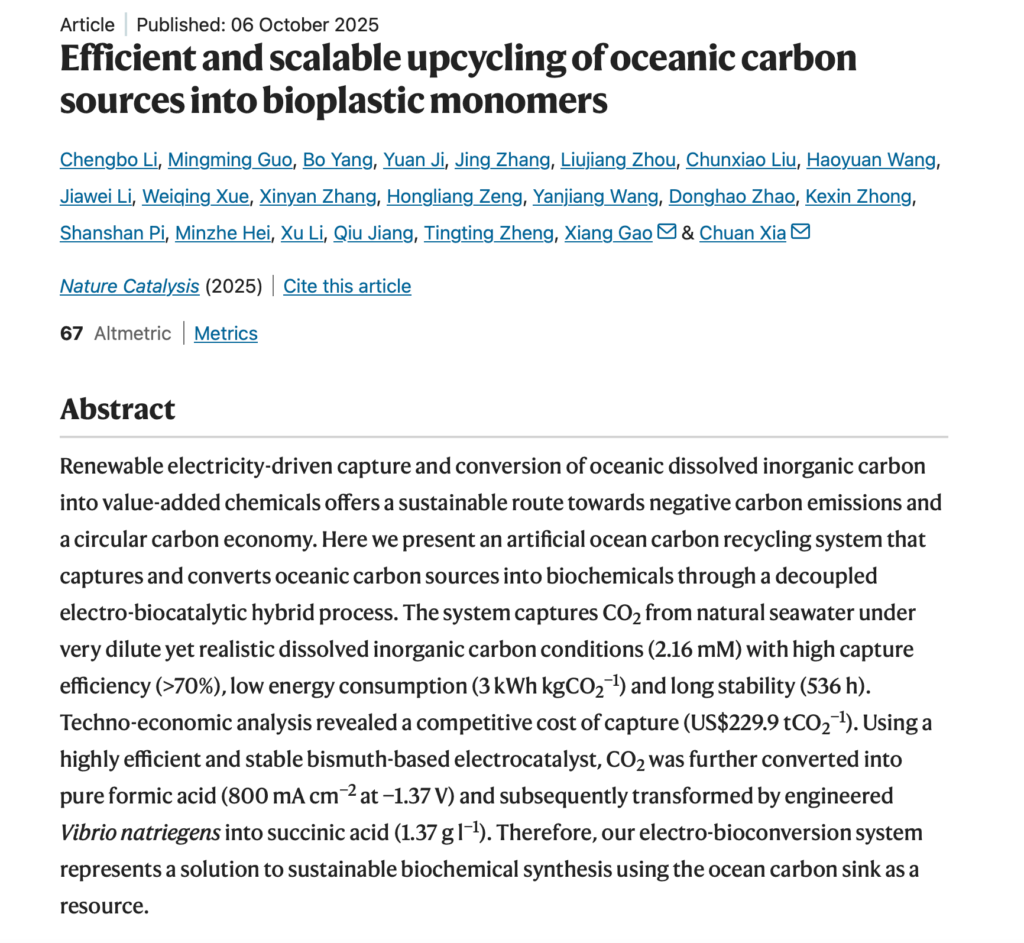
More than five months after the conclusion of negotiations, the upgraded 3.0 version of the China–ASEAN Free Trade Area Protocol was formally signed, marking a new milestone in regional cooperation.
On October 28, during the 47th ASEAN Summit held in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, China and ASEAN signed the 3.0-version upgrade protocol of the China–ASEAN Free Trade Area. Negotiations for the 3.0 upgrade began in November 2022 and reached substantive completion in October 2024. Based on the existing China–ASEAN Free Trade Agreement and the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), this new version further expands mutually beneficial cooperation in emerging areas, strengthens interconnection in standards and regulations, and promotes regional trade facilitation and inclusive development.
The 3.0 upgrade covers nine key fields: the digital economy, green economy, supply-chain connectivity, standards and technical regulations with conformity assessment, sanitary and phytosanitary measures, customs procedures and trade facilitation, competition and consumer protection, micro-, small- and medium-sized enterprises, and economic and technological cooperation. These areas reflect both sides’ determination to lead in the formulation of international rules and to deepen cooperation in new domains.
As China’s first foreign free trade partner and ASEAN’s first FTA partner, the China–ASEAN Free Trade Area has always held a pivotal position in the regional economic landscape. From its early 1.0 stage to the current 3.0 era, the evolution of this partnership demonstrates the steady progress of both sides in promoting regional economic integration. After the signing of the protocol, both parties will complete their domestic ratification procedures to bring the agreement into force as soon as possible.
With this upgrade, China–ASEAN economic cooperation has reached a new starting point. Scholars note that while globalization was once defined primarily by free trade and investment on a global scale, today the trend is shifting toward regional integration. China and ASEAN, as leaders in regional cooperation, have built one of the world’s most dynamic economic relationships. For sixteen consecutive years, China has remained ASEAN’s largest trading partner, while ASEAN has been China’s largest partner for the past five years. The 3.0 version thus reflects not only a higher standard of openness but also a new direction for global economic cooperation led by regional partnerships.
Experts believe that at a time when the global economy faces mounting uncertainty, the signing of this upgraded protocol represents a significant step toward high-quality openness and cooperation. It shows China and ASEAN’s shared commitment to defending the multilateral trading system, countering protectionist trends, and strengthening regional economic resilience through deeper institutional cooperation. For both sides, this means a more stable space for small and medium-sized enterprises and reduced exposure to external risks. The 3.0 version is also a leap beyond tariff reduction: it embodies rule-making, standard integration, and governance innovation — a systemic upgrade that reflects Asia’s capacity to craft its own solutions for regional trade and development.
From focusing on tariff reduction in goods to expanding markets in services, the China–ASEAN Free Trade Area has evolved in scope and sophistication. The 3.0 version marks a fundamental shift — from a “list of goods” approach to one led by “rules and standards.” It introduces mutual recognition of standards within its framework, establishes a unified standard for electronic invoices in digital trade, promotes a “white list” mechanism for cross-border data flows, and creates a carbon-footprint tracing system and photovoltaic component standard recognition in support of green transformation.
Analysts also point out that ASEAN has never been a uniform entity — internal rules and standards vary significantly from one country to another. The 3.0 version seeks to break through these regulatory barriers by fostering convergence in rules. In the field of green economy, for instance, both sides are working to remove trade barriers related to environmental goods and services and to promote mutual recognition of industrial standards, thus facilitating cooperation in green industries and sustainable production capacity.
Under the framework of high-standard rules, China and ASEAN are not only enhancing traditional trade and investment but also broadening collaboration into new sectors. The nine areas covered by the 3.0 upgrade — particularly digital and green economies — are at the heart of global trade transformation. Experts emphasize that these two fields exemplify the complementary advantages between China and ASEAN. In the green economy, for example, Chinese companies in new energy vehicles, photovoltaics, and energy storage are rapidly expanding in Southeast Asia, helping to upgrade local industries and accelerate the region’s green transition. This cooperation not only represents new opportunities for China’s high-tech industries but also injects momentum into ASEAN’s sustainable development.
Despite the current climate of uncertainty in global trade, China and ASEAN have maintained remarkable resilience in their economic relations, sending a clear signal of openness, cooperation, and shared prosperity. According to the General Administration of Customs of China, in the first three quarters of this year, China’s trade with ASEAN reached 5.57 trillion yuan, up 9.6 percent year on year, accounting for 16.6 percent of China’s total foreign trade — reaffirming ASEAN’s position as China’s largest trading partner.
Both sides have long been committed to deepening regional economic integration. Their industrial and supply chains are closely intertwined, with rapid growth in both upstream and downstream trade. As multiple bilateral and multilateral free trade agreements between China and ASEAN members take effect, tariff reductions and trade facilitation continue to deliver tangible benefits, strengthening the integration of regional production networks. In the first three quarters alone, China’s exports of textile machinery and raw materials to ASEAN rose by 28.2 percent and 13.4 percent respectively, while imports of garments increased by 9.3 percent. Imports of rubber from ASEAN surged by 40.7 percent, and exports of tires and auto parts grew by 19.8 percent.
Experts consistently highlight the complementary nature of both sides’ industrial structures. China provides ASEAN with intermediate goods, digital technology, green equipment, and capital, while ASEAN contributes abundant natural resources, labor, and vast emerging markets. China’s technological capability, skilled workforce, and advanced manufacturing combine naturally with ASEAN’s youthful demographics and resource advantages. This synergy allows both sides to maximize their respective strengths.
Such complementarity extends into high-tech sectors. Many Chinese semiconductor companies, for instance, are investing in Malaysia’s Penang region, symbolizing a new wave of two-way industrial cooperation. Institutional frameworks such as RCEP and now CAFTA 3.0 are providing the legal and structural backbone that sustains this dynamic integration.
China’s consistent advocacy of free trade and open regionalism continues to benefit ASEAN economies. As RCEP marks its third anniversary, cooperation between China and ASEAN has grown closer than ever. With China actively pursuing accession to the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) — of which several ASEAN countries are already members — the foundation for broader regional cooperation is steadily expanding.
The signing of the China–ASEAN Free Trade Area 3.0 upgrade protocol thus stands as a landmark achievement. It embodies China’s determination to safeguard multilateralism, deepen institutional openness, and jointly shape the future of regional economic governance with its ASEAN partners. Beyond economic integration, it showcases a distinctly Asian model of cooperation — one rooted in equality, mutual respect, and shared progress — and offers the world a new vision of globalization led not by confrontation, but by collaboration and common development.
Source: Global Times, Reuters, CGTN, ASEAN Main Portal